What is Multidomestic Strategy
A multidomestic strategy is a strategy by which a company operates as stand-alone business units in multiple countries, allowing local subsidiaries in each country to optimize the products or services based on the preferences of local customers and competitive conditions.
The company using a multidomestic strategy uses subsidiaries in each host country to respond to local conditions. Each individual subsidiary has its own function that is required for operating in the local country such as human resources, production, marketing, and research & development functions.
The multidomestic headquarters coordinates only financial controls and some policy, and may centralize some secrets such as R&D and some manufacturing.
A good example of a multidomestic company is the MTV tv show which customizes its show based on the countries, instead of trying to use American MTV for all countries.
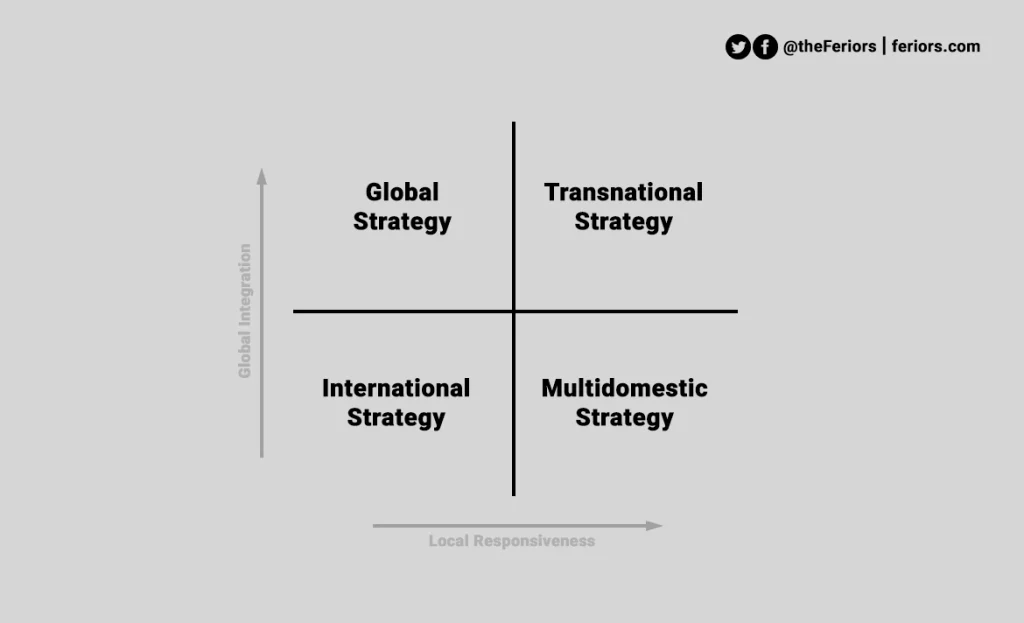
As you can see in the Bartlett & Ghoshal matrix, a multi-domestic strategy ranks high on local responsiveness and low on global integration, the company using a multidomestic strategy is the least pressure for global integration compared with another remaining global integration model. In contrast, the multidomestic company highly adapts to local conditions for competitive advantages.
This makes a multidomestic strategy is the “local-first” approach of the four international business strategies.
The multidomestic strategy is also known as a multinational strategy.
Advantages of Multidomestic Strategy
The advantages of using a multidomestic strategy are the benefit of strong local autonomy in each subsidiary which includes the following advantages:
- Multidomestic subsidiary can customize the products and strategies based on the preferences of local customers and competitive conditions.
- Enables each subsidiary of a multidomestic company to compete independently in different domestic markets.
- Faster for making business decisions against local conditions.
- Less issue about a misunderstanding of difference between cultural, lifestyle, political, and social structure.
- Easily access the competitive advantages from a local resources, such as labor, distribution, and natural resources.
However, the biggest disadvantage of the multidomestic strategy is higher manufacturing costs of forgoing the economies of scale from cost-sharing and centralization, and duplication of effort in each subsidiary since every subsidiary behaves like a strategic business.



