What is Absolute and Comparative Advantage?
Absolute advantage and comparative advantage are international trade theory by Adam Smith and David Ricardo. They’re important international trade theory that influence international business and international trade policy of many countries these day.
To understand what is the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage, first you need to understand the basic concept of absolute advantage vs comparative advantage:
Absolute advantage is suggested that the country had absolute advantage in manufacturing when the country can produce with more efficiently than any other competition. Adam Smith suggested to export these goods for the goods from other countries.
However, the problem of Adam Smith’s absolute advantage is the country can have absolute disadvantage when they can not produce anything with more efficiently. David Ricardo developed the comparative advantage from this issue.
Comparative advantage is an international trade theory that suggested the country had comparative advantage (or relative advantage) when the country can produce a goods or services with lower opportunity cost.
Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage Example
To understand the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage, let’s understand how the abolute advantage theory of Adam Smith works from the following example.
Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage assume that the world had two countries and two product. For this example, suppose that it the United State and the United Kingdom, both equally has 1000 units of resources. The following table is the productivities of both countries.
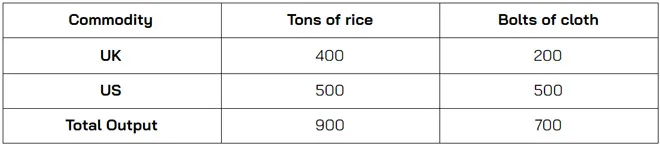
From the table above, the United State has an absolute advantage in both production of rice and cloth, because the United State can produce this product with more quantities (for the same resource as the UK). This is how “Absolute Advantage” works.
Adam Smith will suggest the US to export the absolute advantage goods to trade with absolute advantage goods from the United Kingdom. However, the United Kingdom has no absolute advantage goods. In the other words, the UK has an absolute disadvantage.
This is why David Ricardo developed the Comparative Advantage in 1817. To make a country like the UK able to trade, the comparative advantage theory suggested the country to produce the product that they can produce with lower opportunity cost.
From the example, the United Kingdom is less inefficient in producing rice than cloth compare to the United State.
- Cloth is 40% (2/5) as efficient as the US.
- Rice is 80% (4/5) as efficeint as the US.
Divid Ricardo will suggest the United Kingdom should producing rice, and stop producing cloth and use all resource for producing cloth to empower the production of rice.
What is the Difference Between Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage?
Absolute advantage is concerned about producing a product with a lower cost. Comparative advantage is concerned about producing a product with a lower opportunity cost. However, having an absolute advantage does not mean a country must produce that goods.
Let’s take a look side by side from our summary of the difference between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage below.
Absolute Advantage Summarize
- Absoluted advantage is developed by Adam Smith and publish in his signature book “The Wealth of Nations” in 1776.
- Absoluted advantage is suggested that the country had absolute advantage in manufacturing when the country can produce with more efficiently than any other competition.
- The country need to export these goods for the goods that produce by other countries.
- However, the problem of absolute advantage is the country can has absolute advantage in all goods, while another one has absolute disadvantage in all goods when they can’t produce anything with more efficiently.
- Absolute Advantage is about efficiently.
Comparative Advantage Summarize
- Comparative advantage is developed by David Ricardo and publish in his book “Principles of Political Economy” in 1817.
- The comparative advantage is one step further by exploring what if a country has absolute advantage in the production of all goods, and another one has absolute disadvantage in all goods.
- Comparative advantage is suggested that the country had comparative advantage in manufacturing when the country can produce with lower opportunity cost than any other competition, and export these goods.
- It’s possible for everyone to has a comparative advantage in something.
- Comparative Advantage is about opportunity cost.
The difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage is that the absolute advantage is focused in produce the goods with more efficiently over the competition, while the comparative advantage is focused on the lower opportunity cost in producing a product.




